
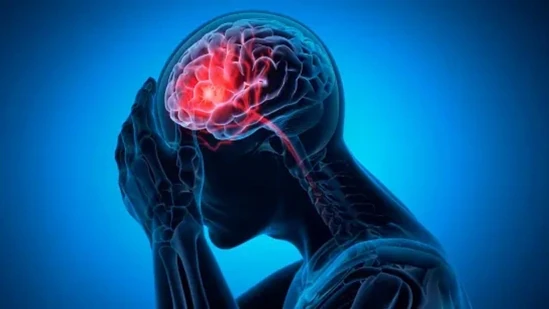
Not All Strokes Come With Pain: Neurologist Warns About Silent Symptoms That Can Save Lives
September 8, 2025 | Health Desk
Strokes are often thought of as sudden, dramatic, and painful events that strike without warning. Images of a person collapsing with one side of their body paralyzed or clutching their head in agony dominate the public imagination. However, neurologists caution that this picture is incomplete. In reality, not all strokes come with pain or obvious symptoms, and many patients fail to recognize the subtle signs until it is too late.
Dr. Brij Lal Choudhary, Consultant Neurology at Manipal Hospital, Jaipur, explained in a recent awareness drive that silent strokes — tiny ischemic episodes in the brain — are far more common than most people realize. “People imagine stroke as a catastrophic event, but often it can be silent, with no severe pain. These are the ones we miss, and they can accumulate over time with serious consequences,” he said.
What Are Silent Strokes?
A silent stroke occurs when blood supply to a small part of the brain is temporarily blocked, causing brain cells in that region to die. Unlike traditional strokes, which typically involve paralysis, speech difficulties, or severe headache, silent strokes may pass unnoticed.
Doctors often discover them incidentally during brain scans for unrelated conditions. Yet the impact is real: each event damages brain tissue and increases the risk of future major strokes, dementia, and cognitive decline.
Studies suggest that up to one-third of older adults show evidence of silent strokes on MRI scans, despite never reporting any classic symptoms.
Subtle Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
According to Dr. Choudhary and other neurologists, some of the early warning signs of a silent or impending stroke include:
Blurred or double vision, particularly sudden changes after screen time or exertion
Unexplained fatigue or fainting spells without clear cause
Memory lapses or confusion, difficulty recalling recent events
Changes in mood or thought process, such as irritability, slow responses, or difficulty concentrating
Balance issues or dizziness, even mild, that appear unexpectedly
Minor headaches that seem unusual for the person
Slurred speech that comes and goes, often mistaken for tiredness
While many of these symptoms can overlap with stress, aging, or lifestyle-related fatigue, neurologists stress that ignoring them can be dangerous. Silent strokes are often cumulative, and over months or years they may lead to significant brain damage.
Why Early Detection Is Critical
The danger of silent strokes lies in their stealth. A patient may not seek medical attention because there is no obvious collapse or pain. However, repeated episodes can cause:
Cognitive decline and dementia (especially vascular dementia)
Reduced mobility and balance, raising the risk of falls
Emotional and behavioral changes, impacting quality of life
Increased risk of a major stroke that could prove life-threatening
Dr. Choudhary emphasizes: “Every silent stroke is a warning shot. It tells us that the brain’s blood supply is compromised. Detecting and acting on these early is key to prevention.”
Diagnosis and Treatment
Silent strokes are often diagnosed through CT or MRI scans. Once identified, treatment focuses on reducing the risk of further episodes:
Controlling blood pressure (a major risk factor)
Managing diabetes and cholesterol through medication and diet
Lifestyle modifications like quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a balanced diet
Anticoagulant or antiplatelet medication, when prescribed by doctors, to prevent clot formation
Rehabilitation therapies (physical, speech, occupational) to strengthen unaffected brain areas
Although brain cells lost in a stroke cannot be regenerated, timely intervention can protect remaining areas and slow decline.
Classic Strokes Still Demand Immediate Action
While silent strokes are stealthy, traditional strokes remain medical emergencies. Doctors use the BE FAST rule to help the public identify urgent signs:
Balance loss
Eye vision changes
Face drooping
Arm weakness
Speech difficulty
Time to call emergency services
If any of these occur, minutes matter. Quick hospital treatment can restore blood flow and reduce long-term disability.
A Growing Public Health Challenge
Silent strokes are more common in people with high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and sedentary lifestyles. They are also linked to sleep apnea, obesity, and smoking. With India witnessing rising cases of lifestyle-related diseases, experts fear silent strokes may become a silent epidemic.
Globally, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that stroke is the second leading cause of death and a major cause of long-term disability. Public awareness campaigns are increasingly focusing not just on dramatic symptoms, but also on subtle, overlooked warning signs.
Final Takeaway
A stroke does not always announce itself with pain or paralysis. Sometimes, it whispers — through fatigue, a fleeting memory lapse, or blurry vision. Listening to those whispers can save lives.
Doctors urge people, especially those with risk factors, to schedule regular health check-ups, monitor blood pressure, and seek medical advice promptly when unusual neurological symptoms appear.
As Dr. Choudhary concluded: “Don’t wait for pain. Stroke prevention begins with awareness. Early detection is the most powerful tool we have.”
Note: Content and images are for informational use only. For any concerns, contact us at info@rajasthaninews.com.
40 के बाद शर्ट से बा...
Related Post
Recent News
Daily Newsletter
Get all the top stories from Blogs to keep track.





_1772986853.png)

_1772896144.png)
_1772893678.jpg)
_1772893476.jpg)