Rise in Fungal Infections in India Raises Public Health Concerns
- bykrish rathore
- 18 November, 2025
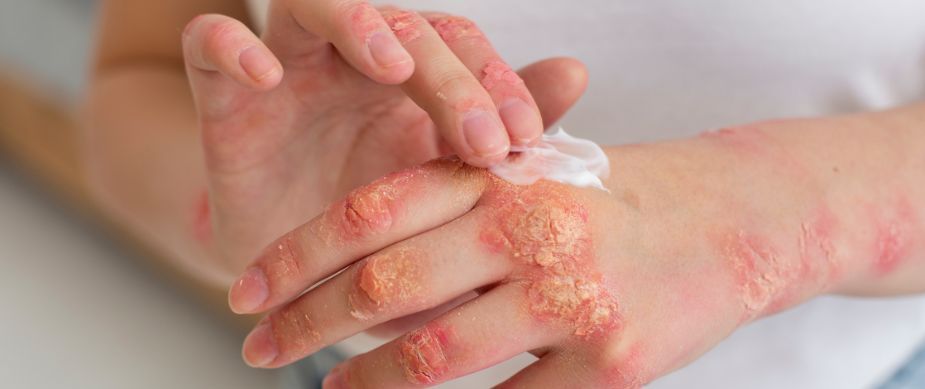
India is experiencing a noticeable and worrying rise in fungal infections, a trend that has drawn the attention of healthcare experts, doctors, and public health authorities. While fungal infections have always existed at low levels, the recent surge is being linked to a combination of environmental changes, weakened immunity among populations, increased antibiotic use, and lingering post-pandemic health vulnerabilities. As cases continue to climb, the situation highlights the urgent need for awareness, timely diagnosis, and improved infection management across the country.
One of the major contributors to this rise is India’s changing climate. Warmer temperatures and higher humidity create ideal conditions for fungi to thrive. Spores become more abundant in the air, increasing exposure for individuals, especially in densely populated areas. Seasonal shifts, pollution, and poor air quality further worsen the spread of fungal pathogens. As fungi adapt and become more resilient, infections that were once considered rare have become more frequent and widespread.
Another important factor driving the increase is compromised immunity among large sections of the population. Patients with diabetes, cancer, HIV, kidney disease, and chronic respiratory conditions face a higher risk of developing severe fungal infections. India has one of the world’s largest diabetic populations, which makes many individuals more vulnerable to invasive fungal diseases such as mucormycosis and candidiasis. The aftermath of COVID-19 has also played a role, as many patients who recovered from severe infections continue to struggle with weakened immune systems. The overuse of steroids during COVID treatment further predisposed individuals to fungal attacks.
In recent years, India has seen more cases of black fungus (mucormycosis), white fungus, aspergillosis, and drug-resistant Candida auris. These infections often start with minor symptoms but can quickly become life-threatening if not treated promptly. Delayed medical attention, self-medication, and limited awareness of early signs contribute to complications. For many patients, diagnosis happens only after the infection has spread, making treatment more difficult and costly.
Antifungal resistance is another growing challenge. Just as bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics, fungi too are becoming harder to treat due to the overuse of antifungal medications in agriculture and healthcare. This resistance reduces the effectiveness of standard treatments and increases the risk of severe outcomes, especially among hospitalized and immunocompromised patients.
Public health experts are urging hospitals and clinics to strengthen surveillance systems to track fungal infections more effectively. Early detection tools, improved laboratory facilities, and specialized training for healthcare workers are essential steps in controlling the rising threat. Public awareness campaigns about hygiene, environmental risks, and the importance of timely medical care can also help reduce the burden.
The rise in fungal infections in India serves as a reminder that diseases beyond viruses and bacteria can pose serious risks. With coordinated health responses, better medical infrastructure, and increased awareness, the country can manage and reduce the spread of these infections while protecting vulnerable communities.
Note: Content and images are for informational use only. For any concerns, contact us at info@rajasthaninews.com.
40 के बाद शर्ट से बा...
Related Post
Recent News
Daily Newsletter
Get all the top stories from Blogs to keep track.





_1772986853.png)

_1772896144.png)
_1772893678.jpg)
_1772893476.jpg)