Global Alarm Over Resurgence of Measles and Whooping Cough Amid Falling Vaccination Rates
- bykrish rathore
- 05 January, 2026
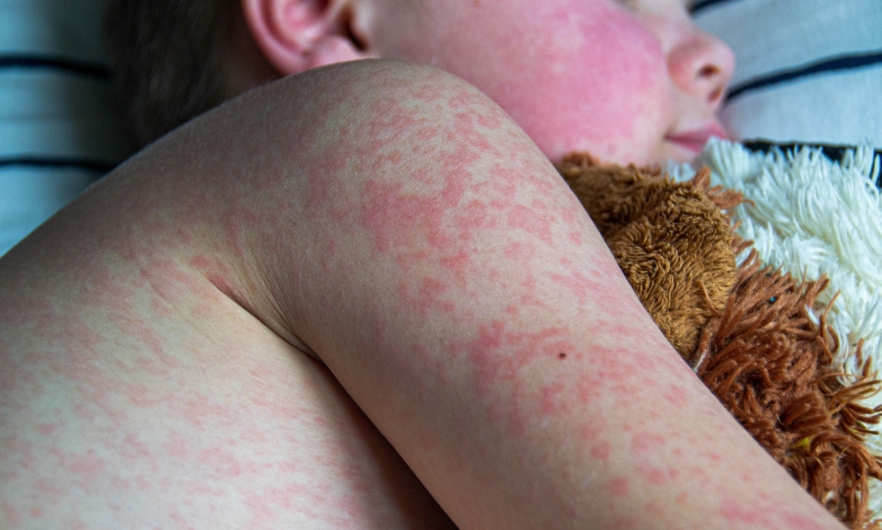
There are growing global and national concerns over the resurgence of measles and whooping cough, also known as pertussis, as public health systems grapple with the consequences of declining vaccination rates and disrupted immunisation programmes. Once considered largely under control in many parts of the world, both diseases are now re-emerging, posing serious risks, particularly to infants, young children, and vulnerable populations.
Measles is one of the most contagious viral diseases known, requiring very high vaccination coverage to prevent outbreaks. Health experts note that even small drops in immunisation rates can lead to rapid spread. In recent years, several countries have reported spikes in measles cases, often linked to communities with low vaccine uptake. Misinformation about vaccine safety and reduced access to healthcare services during the COVID-19 pandemic have significantly contributed to this trend.
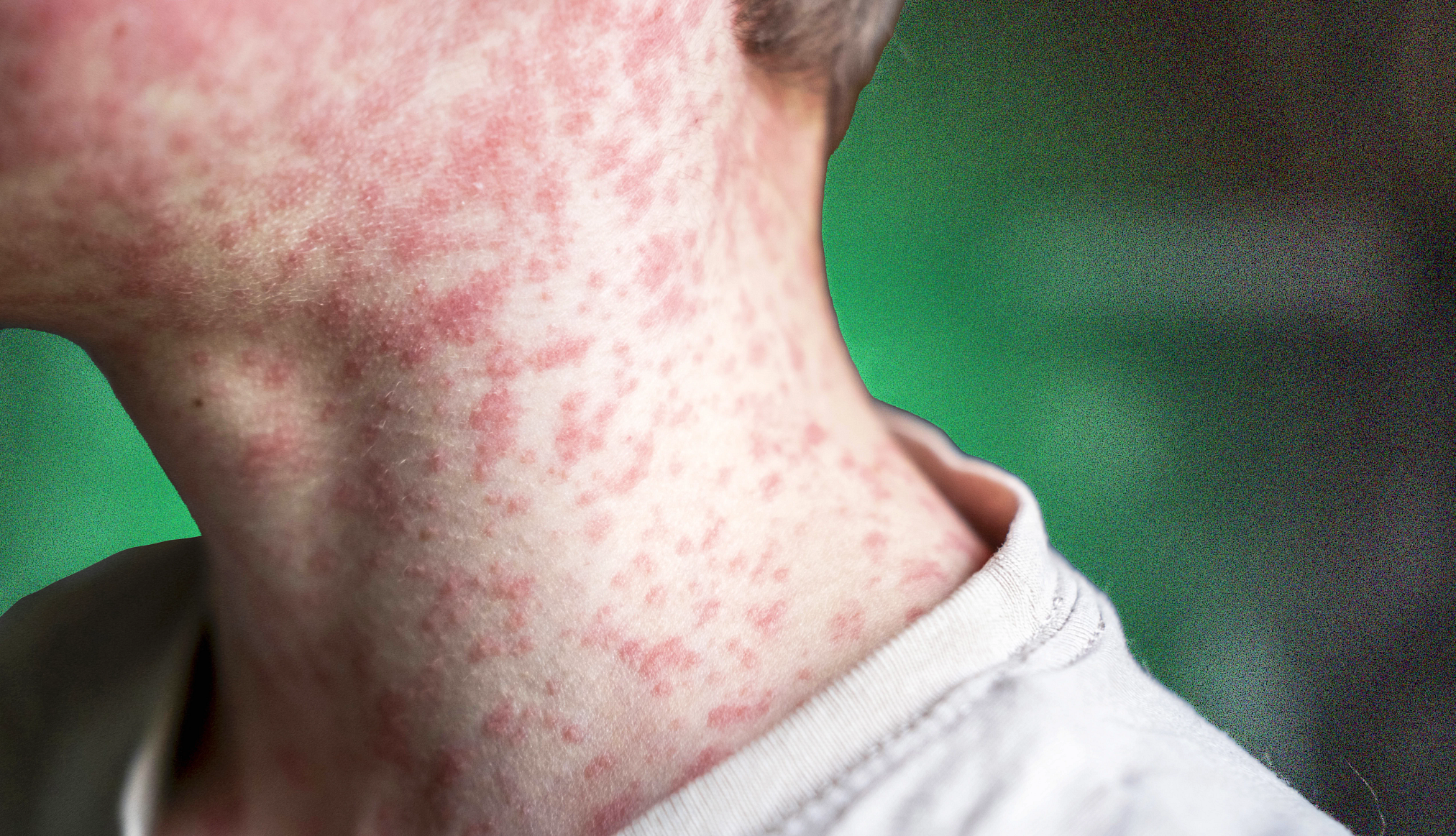
Whooping cough, a bacterial infection that causes severe coughing fits, is also making a worrying comeback. While childhood vaccination offers strong early protection, immunity against pertussis can wane over time. Adults and adolescents with declining immunity may experience mild or unrecognised symptoms, allowing the infection to spread silently to infants who are too young to be fully vaccinated. This has made pertussis outbreaks particularly dangerous for newborns.
Pandemic-related disruptions have played a central role in the resurgence of these vaccine-preventable diseases. Lockdowns, overwhelmed health systems, and the redirection of resources toward COVID-19 response led to missed routine immunisation appointments across many countries. According to public health experts, millions of children worldwide did not receive scheduled vaccines during this period, creating immunity gaps that are now being exploited by infectious diseases.
National health authorities are increasingly urging governments to strengthen surveillance systems, restore routine vaccination services, and launch catch-up immunisation campaigns. Special emphasis is being placed on reaching underserved and hesitant populations, where coverage gaps are often widest. In addition, experts stress the importance of booster doses for adults, particularly for whooping cough, to reduce transmission within households and communities.
The resurgence of measles and pertussis also serves as a reminder of the interconnected nature of global health. In an era of international travel, outbreaks in one region can quickly spread across borders. Maintaining high vaccination coverage is therefore not only a national responsibility but a global necessity.
Public health professionals warn that without urgent action, outbreaks could become more frequent and severe. Strengthening trust in vaccines, countering misinformation, and ensuring equitable access to immunisation services are seen as critical steps in reversing the current trend.
In conclusion, the re-emergence of measles and whooping cough underscores the long-term consequences of disrupted vaccination systems. As health authorities work to rebuild immunisation coverage, the situation highlights a clear lesson: sustained commitment to routine vaccination is essential to prevent the return of diseases that are both preventable and potentially deadly.
Note: Content and images are for informational use only. For any concerns, contact us at info@rajasthaninews.com.
40 के बाद शर्ट से बा...
Related Post
Recent News
Daily Newsletter
Get all the top stories from Blogs to keep track.





_1772986853.png)

_1772896144.png)
_1772893678.jpg)
_1772893476.jpg)